Eye Allergies: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Allergic Conjunctivitis
Eye Allergies: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Allergic Conjunctivitis
Our eyes are sensitive organs that allow us to see and experience the world around us. However, for millions of people, the changing of seasons or exposure to allergens can turn this blessing into a source of discomfort and frustration. Allergic conjunctivitis, often referred to as eye allergies, is a common condition that can cause itching, redness, tearing, and other uncomfortable symptoms. Fortunately, with the right knowledge and strategies, you can effectively manage and prevent allergic conjunctivitis. In this comprehensive 5000-word guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of eye allergies, equipping you with the tools you need to enjoy clear and comfortable vision year-round.
Chapter 1: Understanding Allergic Conjunctivitis
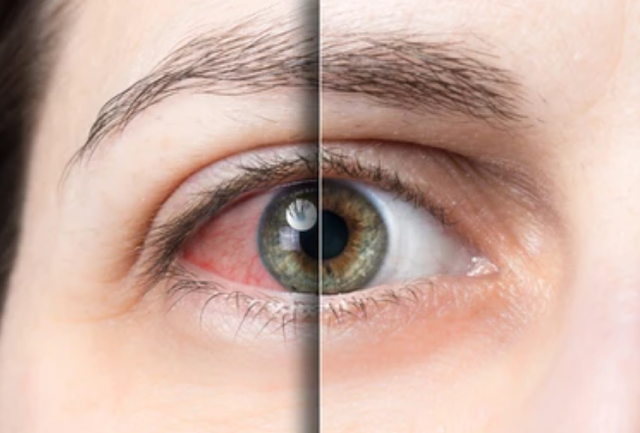
Before we explore how to manage and prevent allergic conjunctivitis, it's important to understand the condition itself. Allergic conjunctivitis is characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelid. This inflammation is triggered by exposure to allergens, which are substances that the immune system perceives as harmful, even though they are typically harmless.
Chapter 2: Types of Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Seasonal Allergic Conjunctivitis (SAC): As the name suggests, SAC occurs during specific seasons, such as spring and fall, when allergens like pollen are prevalent. It is often associated with other seasonal allergies like hay fever.
- Perennial Allergic Conjunctivitis (PAC): PAC can occur year-round and is typically caused by indoor allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and mold.
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC): VKC is a more severe form of allergic conjunctivitis that primarily affects young males. It tends to occur seasonally and is characterized by intense itching, thick discharge, and the formation of small, raised bumps on the conjunctiva.
- Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis (AKC): AKC is a chronic form of eye allergy that is often associated with atopic dermatitis (eczema). It can cause significant eye discomfort and damage if left untreated.
Chapter 3: Common Allergens
Allergic conjunctivitis can be triggered by a wide range of allergens. Some of the most common include:
- Pollen: From trees, grasses, and weeds, pollen is a major seasonal allergen.
- Dust Mites: These microscopic creatures thrive in household dust and can be a year-round allergy trigger.
- Pet Dander: Proteins found in the skin cells, urine, and saliva of pets can trigger allergies in susceptible individuals.
- Mold: Mold spores, often found in damp environments, can be inhaled or come into contact with the eyes, causing irritation.
- Cigarette Smoke: Smoke and other air pollutants can exacerbate allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
- Contact Lenses: Improper use or cleaning of contact lenses can lead to the accumulation of allergens and exacerbate eye allergies.
Chapter 4: Symptoms of Allergic Conjunctivitis
Recognizing the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis is crucial for early intervention and relief. Common symptoms include:
- Itching: One of the hallmark symptoms, itching of the eyes can be intense and persistent.
- Redness: The eyes may appear bloodshot due to inflammation.
- Tearing: Excessive tearing, or watery eyes, is a common response to irritation.
- Swelling: The eyelids may become puffy and swollen.
- Burning Sensation: Some individuals describe a burning or stinging sensation in the eyes.
- Stringy Discharge: A clear or white discharge may accumulate in the corners of the eyes.
- Light Sensitivity: Photophobia, or sensitivity to light, can be present.
Chapter 5: Diagnosis of Allergic Conjunctivitis
If you suspect you have allergic conjunctivitis, it's essential to seek a proper diagnosis from an eye care specialist. The diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: Your doctor will inquire about your symptoms, their duration, and any potential triggers or allergies.
- Eye Examination: A thorough examination of your eyes, including the use of a slit lamp, will be performed to assess the extent of conjunctival inflammation.
- Allergy Testing: In some cases, allergy testing, such as skin tests or blood tests, may be recommended to identify specific allergens.
Chapter 6: Managing Allergic Conjunctivitis
Effective management of allergic conjunctivitis involves both short-term relief of symptoms and long-term strategies to prevent recurrences. Treatment options include:
- Artificial Tears: Lubricating eye drops can help relieve dryness and flush out allergens from the eyes.
- Antihistamine Eye Drops: These over-the-counter or prescription eye drops can provide relief from itching and redness.
- Decongestant Eye Drops: These drops can help reduce eye redness but should be used sparingly, as long-term use can worsen symptoms.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Prescription corticosteroid eye drops can effectively reduce inflammation but should only be used under the supervision of an eye care professional due to potential side effects.
- Oral Antihistamines: These medications can alleviate systemic allergy symptoms but may not directly address eye discomfort.
- Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress to closed eyes can provide relief from itching and swelling.
- Avoid Allergen Exposure: Whenever possible, minimize exposure to allergens by keeping windows closed, using air purifiers, and regularly cleaning your living space.
Chapter 7: Prevention Strategies
Preventing allergic conjunctivitis is an essential part of managing the condition and improving your quality of life. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Identify Allergens: Work with your healthcare provider to identify specific allergens that trigger your symptoms. Once identified, take steps to reduce your exposure.
- Allergen Avoidance: When allergens are identified, take steps to minimize exposure. For example, use allergen-proof covers on pillows and mattresses to reduce exposure to dust mites.
- Wear Sunglasses: Wraparound sunglasses can help protect your eyes from airborne allergens.
- Limit Contact Lens Use: If you wear contact lenses, consider limiting their use during allergy seasons and following proper cleaning and storage guidelines.
- Keep Windows Closed: During peak allergy seasons, keep windows closed to prevent allergens from entering your home.
- Air Purifiers: Consider using air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove allergens from indoor air.
- Wash Hands and Face: After outdoor activities, wash your hands and face to remove allergens.
- Change Clothes: Change and wash your clothes after spending time outdoors to avoid bringing allergens indoors.
Chapter 8: When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of allergic conjunctivitis can be managed with over-the-counter remedies and lifestyle changes, there are instances when you should seek immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe eye pain, vision changes, or worsening symptoms despite treatment, consult an eye specialist.
- Signs of Infection: Symptoms such as pus-like discharge, crusting of the eyelids, or fever may indicate an eye infection that requires prompt medical attention.
- Non-Allergic Causes: If you are unsure whether your symptoms are due to allergies or another eye condition, consult an eye care professional for a proper diagnosis.
Chapter 9: Living with Allergic Conjunctivitis
Living with allergic conjunctivitis requires ongoing management and adaptation to changing seasons and environments. Here are some additional tips for maintaining your eye health:
- Stay Informed: Keep track of local pollen counts and allergen levels to anticipate when your symptoms may worsen.
- Medication Management: If you are prescribed medication, follow your doctor's instructions carefully, and keep track of any side effects.
- Eye Hygiene: Maintain good eye hygiene by avoiding rubbing your eyes, washing your hands frequently, and avoiding touching your face.
- Eye Protection: Consider protective eyewear, such as goggles or wraparound sunglasses, when engaging in outdoor activities.
- Consult Your Doctor: If your symptoms persist or worsen over time, consult your eye care specialist for a reassessment and potential adjustment of your treatment plan.
Chapter 10: Conclusion
Allergic conjunctivitis can be a nuisance, but with the right strategies and guidance, you can effectively manage and prevent its symptoms. Whether you experience seasonal or year-round allergies, understanding your triggers and taking proactive steps to reduce exposure can significantly improve your quality of life. Remember that seeking the advice of an eye care specialist is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. With proper care and precautions, you can enjoy clear and comfortable vision, even in the midst of allergy season.
















No comments