What Are Free Radicals? How They Affect the Body: Properties, Sources, Targets, and Their Implications
What Are Free Radicals? How They Affect the Body: Properties, Sources, Targets, and Their Implications
Free radicals are a complex yet crucial aspect of our body's biochemistry, playing a pivotal role in both health and disease. These highly reactive molecules are integral to various physiological processes but can also wreak havoc when present in excess. In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the mysteries of free radicals, exploring their properties, sources, their interaction with biological targets, and the implications of free radical activity on human health.
Section 1: Understanding Free Radicals
- Defining Free Radicals - Provide a clear definition of free radicals, explaining their chemical nature and structure.
- Electron Imbalance - Explain the central concept of electron imbalance that makes free radicals highly reactive.
Section 2: Properties of Free Radicals
- Reactivity - Detail the extreme reactivity of free radicals, highlighting their potential for damage.
- Oxidative Capacity - Discuss the oxidative capacity of free radicals and their role in oxidation-reduction reactions.
- Stability and Short Lifespan - Explain the relatively short lifespan of free radicals due to their inherent instability.
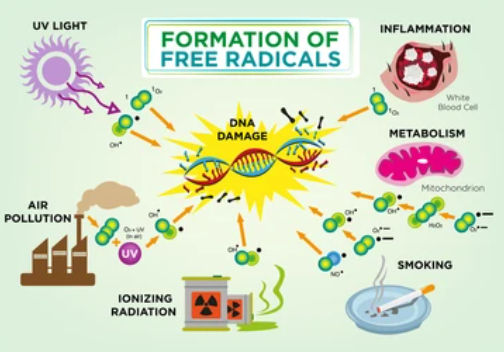
Section 3: Sources of Free Radicals
- Metabolic Processes - Explore how free radicals are naturally produced during metabolic processes, such as cellular respiration.
- Environmental Factors - Discuss external sources of free radicals, including exposure to pollutants, radiation, and certain chemicals.
- Inflammation and Immune Response - Explain how free radicals are generated as part of the body's immune response and inflammation.
Section 4: Biological Targets of Free Radicals
- Lipids - Discuss how free radicals can damage lipids in cell membranes through lipid peroxidation.
- Proteins - Explore the impact of free radicals on protein structure and function, including protein oxidation.
- DNA - Examine the consequences of free radical-induced DNA damage and mutations.
- Antioxidant Defense System - Describe the role of the body's antioxidant defense system in protecting against free radical damage.
Section 5: Implications of Free Radicals on Health
- Oxidative Stress - Define oxidative stress and its role in various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Aging - Discuss the connection between free radical-induced cellular damage and the aging process.
Section 6: Antioxidants: Nature's Defense Against Free Radicals
- What Are Antioxidants? - Explain the role of antioxidants in neutralizing free radicals and maintaining balance.
- Sources of Antioxidants - Explore dietary sources of antioxidants, including vitamins (e.g., vitamin C, vitamin E), minerals (e.g., selenium, zinc), and phytochemicals (e.g., flavonoids, polyphenols).
Section 7: Free Radicals and Disease
- Cardiovascular Diseases - Examine how oxidative stress contributes to the development of heart disease and stroke.
- Cancer - Discuss the role of free radicals in DNA damage and cancer initiation.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders - Explore the connection between oxidative stress, free radicals, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- Inflammatory Conditions - Explain the involvement of free radicals in chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Section 8: Strategies for Reducing Free Radical Damage
- Dietary Approaches - Discuss dietary strategies to increase antioxidant intake and reduce free radical damage.
- Lifestyle Modifications - Explore lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress reduction, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption to mitigate oxidative stress.
- Supplements - Address the role of antioxidant supplements in managing oxidative stress and free radical damage.
Section 9: Measuring Oxidative Stress
- Biomarkers - Describe biomarkers used to assess oxidative stress in clinical settings.
- Laboratory Tests - Explain laboratory tests that can quantify free radical damage, including assays for lipid peroxidation and DNA damage.
Section 10: Future Research and Therapies
- Emerging Research - Highlight current research areas exploring the role of free radicals in health and disease, as well as potential therapeutic interventions.
- Advanced Antioxidant Therapies - Discuss innovative antioxidant therapies and their potential for managing conditions related to oxidative stress.
Section 11: Conclusion
Free radicals are a double-edged sword in the intricate world of human biology. While they are essential for many physiological processes, their excessive presence can lead to cellular damage, disease, and aging. Understanding the properties, sources, targets, and implications of free radicals provides a foundation for making informed choices to reduce oxidative stress and promote overall health.
Through a balanced approach that includes a healthy diet, lifestyle modifications, and, when appropriate, antioxidant supplements, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate the harmful effects of free radicals and promote well-being. As scientific research continues to advance, our knowledge of free radicals and their impact on health will evolve, potentially leading to new therapies and interventions that harness the power of antioxidants to combat the ravages of oxidative stress.
















No comments